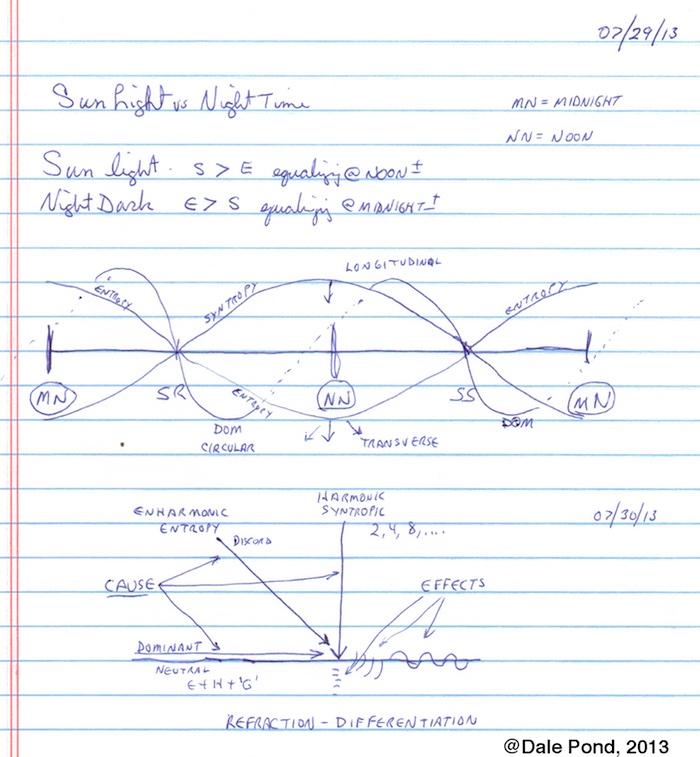
Figure 8.3 - Coiled Spring showing Longitudinal Wave
- Same as Compression Wave or Sound Wave. A wave incident or normal to a surface. One of many modes or dimensions of motion present in all vibrations and oscillations. Generally, considered as a motion to and from a center or source. When harmonic is considered syntropic and when enharmonic considered entropic.
- "Vibration in which the principal motion is in the direction of the longest dimension." (Rossing, Thomas D.; The Science of Sound; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1982.)
- "A vibrating medium must lengthen and shorten 2 times per each lateral (transverse) oscillation; so 1 longitudinal equals 2 lateral or (transverse). Longitudinal frequencies are independent of string tension." (Tyndall, John; Sound; Longmans, Green, and Co., London, 1893.)
Longitudinal Axis
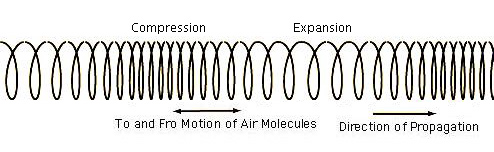
Triple axis of the three modes of vibration drawn to reference a circle and sphere.
The three modes working together develop rotation by and through each other's motion - the rotation is the Rayleigh Wave or Surface Wave mode. The first two modes cause (or are) straight line and zig-zag motions only. The third or Rayleigh Wave is circular.
Longitudinal Axis
Longitudinal Waves, Velocity of
See Also
8.3 - Conventional View of Wave Motion
Compression Wave
Compression Wave Velocity
Figure 8.2 - Compression Wave Phase Illustration
Figure 9.11 - Compression Wave with expanded and contracted Orbits
Longitudinal Wave
Modes of Vibration
Sine Wave
Sound
Wave
Wave Field
CityU physicists discovered special transverse sound wave
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/937147
See Also
counter-reactive transverse electrical potentials
Figure 8.4 - Transverse Wave
horizontal
horizontally radiating
transverse
transverse axis
Transverse Wave
Perhaps one of the more interesting aspects of Keely's work is his Wave Function. The Wave Function is comprised of those foundational forces creating all oscillation and vibration which are seen effects of those unseen causes. Fundamentally these forces are in the 3, 6 and 9 proportions discussed in the "Laws of Being - Annotated" and "Modes of Vibration - Annotated".
Table 13.01 - Suppositional Math and Symbolic Structure
A
= ATH = IA(3+) + IA(4±) + IA(3-) (Harmonic Current) |
| Where..., Currents Hc = Harmonic current = 3+ Ec = Enharmonic current = 3- Dc = Dominant current = 4± |
| Streams Hs = Harmonic stream = 3+ Es = Enharmonic stream = 3- Ds = Dominant stream = 4± |
| Subdivisons
of Matter M = Molecular subdivision IM = Intermolecular subdivision AT = Atomic subdivision IA = Interatomic subdivision E = Etheric subdivision IE = Interetheric subdivision CIE = Compound Interetheric subdivision |
See Also
Table 2 - Controlling Modes and Proportions
| Governing Mode | Subservient Mode | ||
| 3 - Molecular | 100 x Enharmonic | 66 2/3 Harmonic | 33 1/3 Dominant |
| 6 - Atomic | 100 x Harmonic | 66 2/3 Enharmonic | 33 1/3 Dominant |
| 9 - Etheric | 100 x Dominant | 66 2/3 Harmonic | 33 1/3 Enharmonic |
| Thirds | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Proportion | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 |
| Portion |
Does Feynman's morphology depict Keely's above 1/3 and2/3 Controlling Mode concepts?
Figure 7B.09 - Feynmans Triplet Structure of Photon
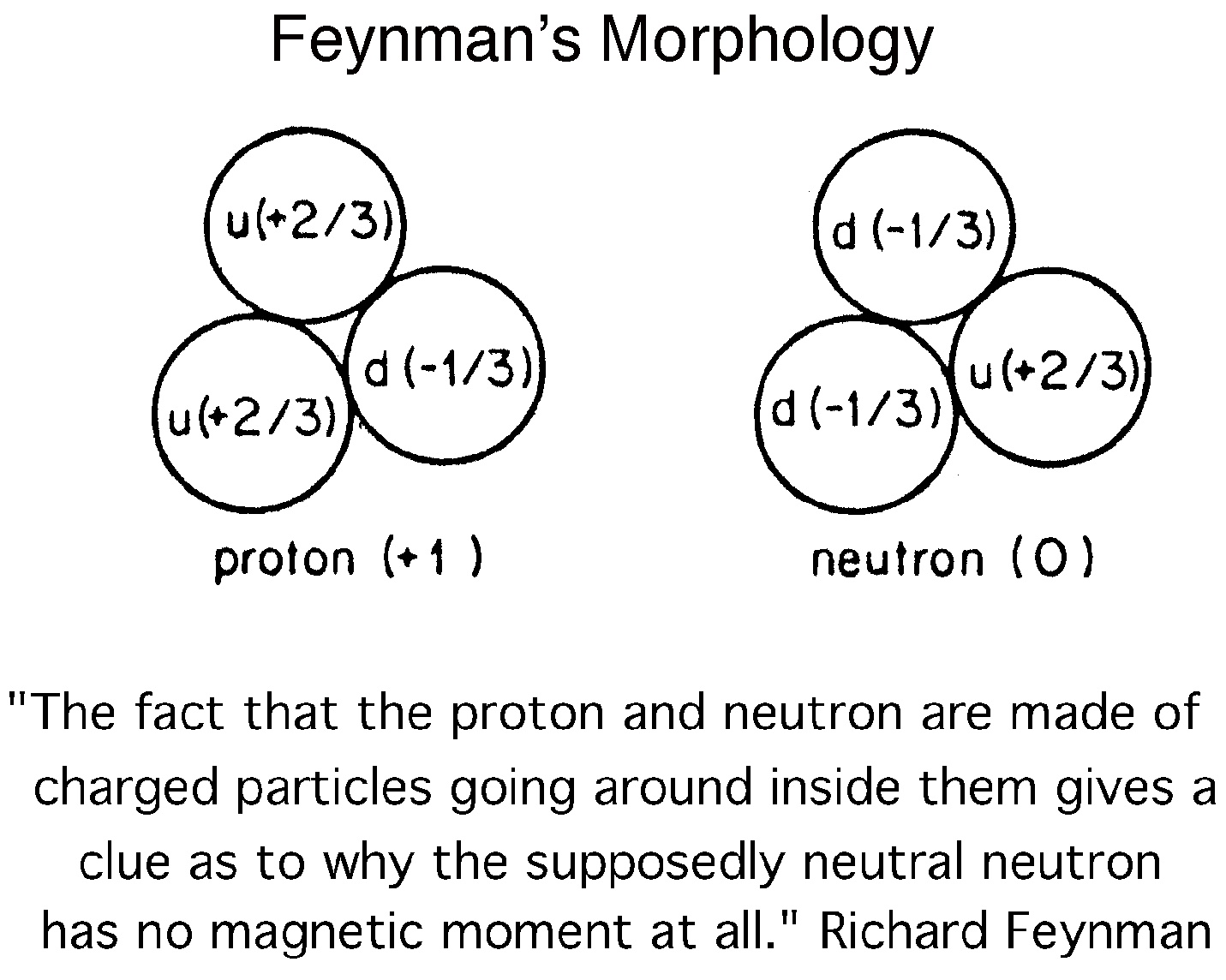
Table 14.03 - Ranges of Forces Vibration Forms Types and Governing Laws
| Range[1] | cps range (gamut) | Sound Type | Sound Effect | Sound Action | Vibe Type | Governing Law | |
| 65..105 | ? - ? | Atoms Oscillate | |||||
| 43..64 | 4,398,046,511,104 / 1.8014398509482E+19 | Atoms Oscillate | |||||
| 21..42 | 2,097,152 / 4,294,967,296,000 | Internal Vibrations | |||||
| 1..20 | 1... 1,048,576 |
Keely
"The laws governing the polar current are intimately concerned in the phenomena of rotation." [POLAR CURRENT]
[1] see Subdivision
[NOTE: 06/29/13; CPS needs to be recalculated]
Keely
"The circles containing the sensitized disks - both polar and depolar - are in sympathetic relation to the polar negative circuits of the earth, and in a condition to be brought into action by the negative transmitter. The sympathetic conditions of the polar and depolar field of the circuits remain latent until the transmitter is associated and the introductory impulse given. Then conditions assert themselves which demonstrate the wonderful power of sympathetic action in abeyance to the laws by which they are governed." [The Operation of the Vibratory Circuit]
| Source | Away from Center | To Center | Balancing or Controlling |
| Keely / SVP[6] | |||
| Modern wave form | Longitudinal[2] | Transverse[3] | Raleigh[1] |
| Angle of Incidence | 0°-45° | 45°-90° | >90° |
| Path/Motion[3] | Straight | Zig-zag | Circular |
| Keely / SVP | |||
| Keely / SVP | |||
| Russell[4] | |||
| Russell[4] | |||
| Charles Henry[7] | |||
| Possible Correspondence[5] |
[1] Also called Circular wave, Curl, Love Wave, Lamb Wave, Surface wave, Etheric. "Power of rotation comes on the positive and power of negation, arising when the receptive flows become independent of the circular chord of resonation (set up mechanically or otherwise) breaks up the rotational power." [ROTATION - Snell]
[2] Also called Compression wave. "The vibratory velocity governing the magnetic flow ranges from 300,000 to 780,000 per second and comes under the first interatomic. This is the first order above odor and permeates the molecules of glass in the compass cover as air passes through a sieve. Being governed by the full harmonic chord this flow moves in straight lines free from molecular interference. [MAGNETIC ENGINE - Snell] "when free of this differentiation are in straight lines." [Discordant]
Figure 8.3 - Coiled Spring showing Longitudinal Wave
[3] "Discordance in any mass is the result of differentiated groups, induced by antagonistic chords, and the flight or motions of such, when intensified by sound, are very tortuous and zig-zag;" [Discordant]
[4] See Wave Field
- 12.05 - Three Main Parts of a Wave
- 12.09 - The MINUS side
- 12.08 - The PLUS side
- Figure 2.12.1 - Polarity or Duality
- Figure 15.03 - Opposing Forces of Gravity and Radiation
- 7B.16 - Polarity, Principle of Polarity
[5] Artwork by JP et al. and this diagram: Triple Modes [6] The Seven Subdivisions of Matter and Energy, VACUUMS FROM VIBRATORY INDUCTION [7] Jose Arguelles, Earth Ascending, page 21; 1996 (3rd edition) [See Binary Triplet]
[See MUSICAL CHORDS, Triplet]
Keely's Three Modes of Vibration
| Subdivision[6] | Octave [Hz = 2octave] | ||
| 1-21 | |||
| 21-42 | |||
| 42-63 |
"By use of the dominant mode, which is allied to the "order" of etheric vibrations, we can induct, "sympathetic negative attraction" or "sympathetic positive propulsion" in any mass, according to its mass chord." [SYMPATHETIC INDUCTION - Snell]
See Also
02 - The Transmission of Sound
1.14 - Materiality from Immateriality
1.21 - It Really Is a Musical Universe
3.11 - Introductory Impulse
3.13 - Reciprocals and Proportions of Motions and Substance
3.8 - There are no Waves
4.2 - Triple Vectors and Rotation
6.8 - Proportionate and Relative Geometries
9.12 - Velocity of Sound and its Propagation Rate are Proportional
9.20 - Center and Periphery
12.00 - Reciprocating Proportionality
12.04 - Locked Potentials and the Square Law
12.05 - Three Main Parts of a Wave
12.07 - Keelys Thirds Sixths and Ninths
13.00.01 - Vibratory Rotation
13.15 - Principle of Proportion
14.04 - Thirds as Currents
14.09 - Brintons Laws of Being
14.29 - Force and Energy Defined
14.35 - Teslas 3 6 and 9
14.35.1 - Keely 3 6 and 9
15.05 - Relative Diameters in Dissociation
16.24 - Triune Vibratory States or Conditions
17.13 - Gravity or Levity
19.04 - Rotation from Vibration
Acoustic Levitation
Akasa - Ether: The First Duality
Alchemy - Most Sacred Science
angle of incidence
Apergy - Power Without Cost
Are Physical and Spiritual Energies Identical
Binary Triplet
Chapter I - The Mental Dynamo
Color
Curl
Dynamics of Mind
Enharmonic
Ether
Ether the True Protoplasm
Etheric Force Identified as Dynaspheric Force
Figure 1.12 - Naturally Occurring Frequencies Modes and Music Interval Relations
Figure 13.15 - Equilibrium as Musical Tonal Equivalents
Figure 13.17 - Focalizing and Reradiating mode of Sympathetic Transmission
Figure 2.12.1 - Polarity or Duality
Figure 2.3 - Focalizing and Reradiating mode of Sympathetic Transmission
Figure 4.3 - Single Mode Electric Vector Generating Circular Motion also Shown within Triple Vectors
Figure 4.3 - Single Mode Electric Vector Generating Circular Motion also Shown within Triple Vectors - See Also
Figure 5.4 - Vortex and Gyroscopic Motion on One Plane then on three forming Sphere
Figure 7.1 - Step 1 - Wave Vortex Crests at Maximum Polarization
Figure 8.14 - Some Basic Waveforms and their constituent Aliquot Parts
Figure 9.11 - Compression Wave with expanded and contracted Orbits
First Cause
Flyback Transformer
Force-Atomic
Gravity
Harmonic
impulse
Interference
Introduction
Keely and Science - Part 2
Keely WaveFunction
Keelys Physical Philosophy
KEELYS PHYSICAL PHILOSOPHY - Snell
Keelys Secrets - Part 2 - One Phase of Keelys Discovery in Its Relation to the Cure of Disease
Law of Corporeal Vibrations
Law of One
Law Suit
Laws of Being
Laws of Being - Annotated
LAWS OF ENERGY
Laws of Music
Levitation
Locked Potentials and the Square Law
Longitudinal
Longitudinal Wave
mass
MASS VIBRATIONS
Mind Force is a pre-existing Natural Force
minor
Mode
Modes of Vibration - Annotated
Molecular Dissociation
More on Keelys Theories
music note or sound colors
MUSICAL CHORDS
Neutral Center
Newton of the Mind
PERMANENCE OF FORM AND MATTER
Phase
Phase Velocity
Principles of Acoustics
Proportion
Pythagoras
Quantum Arithmetic Elements
Rayleigh Wave
Ratio
Rotation
ROTATION - Snell
ruling vibratory mode
Scientific Creation
sense
Sketch of a Philosophy
sympathetic celestial streams
Sympathetic Coincidence
Table 13.01 - Suppositional Math and Symbolic Structure
Table 14.04 - Occurrences of the term dominant in SVP Keely files
Table 2 - Controlling Modes and Proportions
Tables
The Coming Force
The Laws of Being
The Keely Motor Bubble
The Keely Motor Secret
The Key to the Problems. - Keelys Secrets
The Moray Valve Manuscript
THE NEUTRAL CENTER - Snell
Three Laws of Being
universal ratios
Veil Withdrawn
Vibratory Induction
Vril
Wolf Tone
