| Battery | Battery | |
Sympsionics Symbol | ||
Electricity-producing cells which use interaction of metals and chemical to create electrical current flow.
An electrical battery is a combination of two or more electrochemical cells used to convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy.
There are two types of batteries: primary batteries (disposable batteries), which are designed to be used once and discarded when they are exhausted, and secondary batteries (rechargeable batteries), which are designed to be recharged and used multiple times. (Wikipedia)
In common usage, the word "battery" has come to include a single galvanic cell, but a battery properly consists of multiple cells.
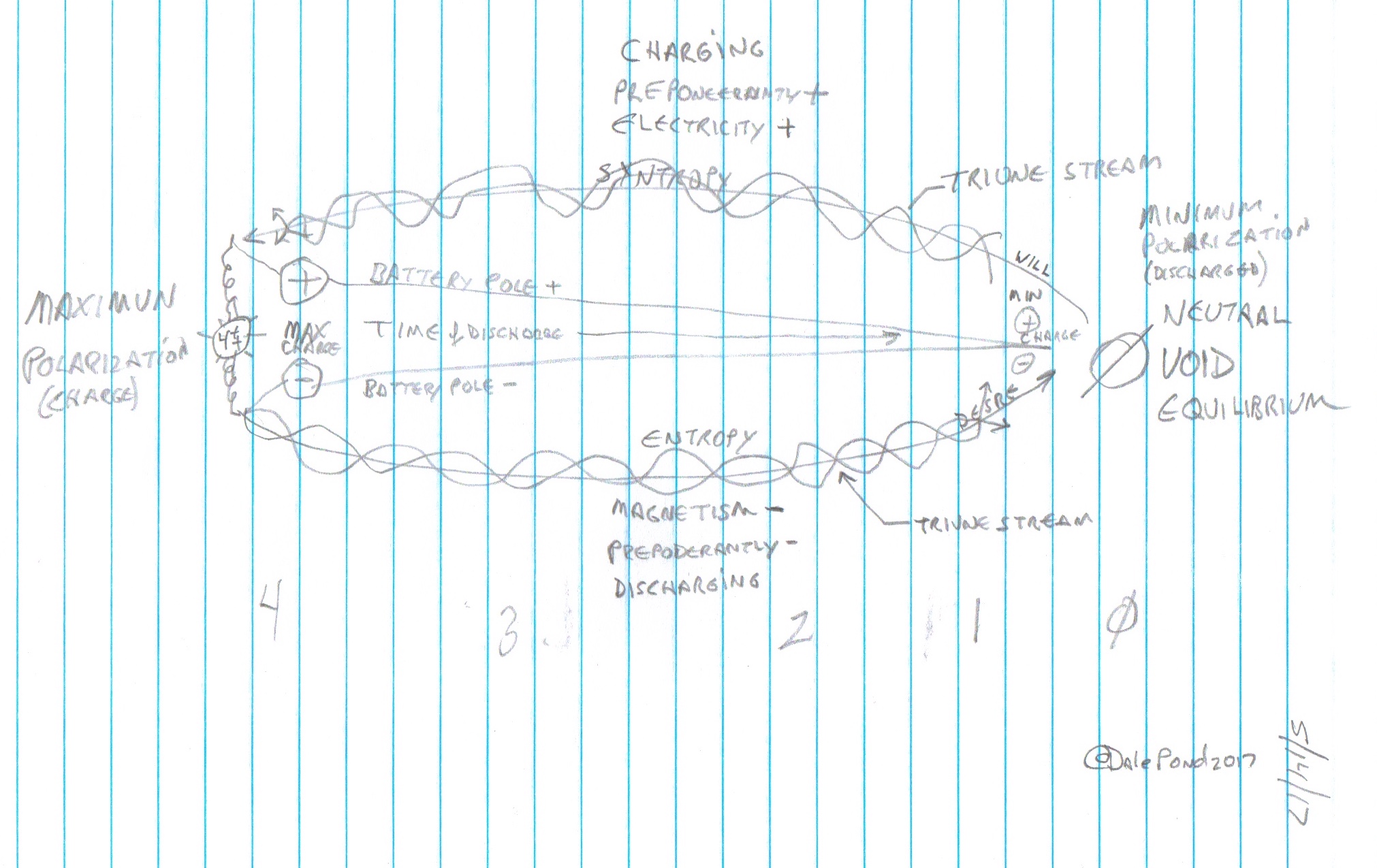
Charge and Discharge Cycle (click to enlarge)
Cobalt-Lithium
Most lithium-ion batteries for portable applications are cobalt-based. The system consists of a cobalt oxide positive electrode (cathode) and a graphite carbon in the negative electrode (anode). One of the main advantages of the cobalt-based battery is its high energy density.
[See CAUSE OF THE UNIVERSAL PULSE BEAT and New Concept - V - This Electric Universe of Simulated Energy for details about batteries according to Russell.]
See Also
Capacity
Capacitor
Charge
CAUSE OF THE UNIVERSAL PULSE BEAT
Discharge
__dry cell battery
electrical affinity
Electricity
electromotive force
Electromotive Series
Faraday
Forever Battery
Galvani, Luigi
Galvanic Cell
Genero-Radiative Concept
Laws of Electrolysis
Magnetism
New Concept - V - This Electric Universe of Simulated Energy
Polar
Polarity
Volt
Voltaic Pile
Volta, Alessandro
What Electricity Is - Bloomfield Moore
zinc copper iron electrochemistry