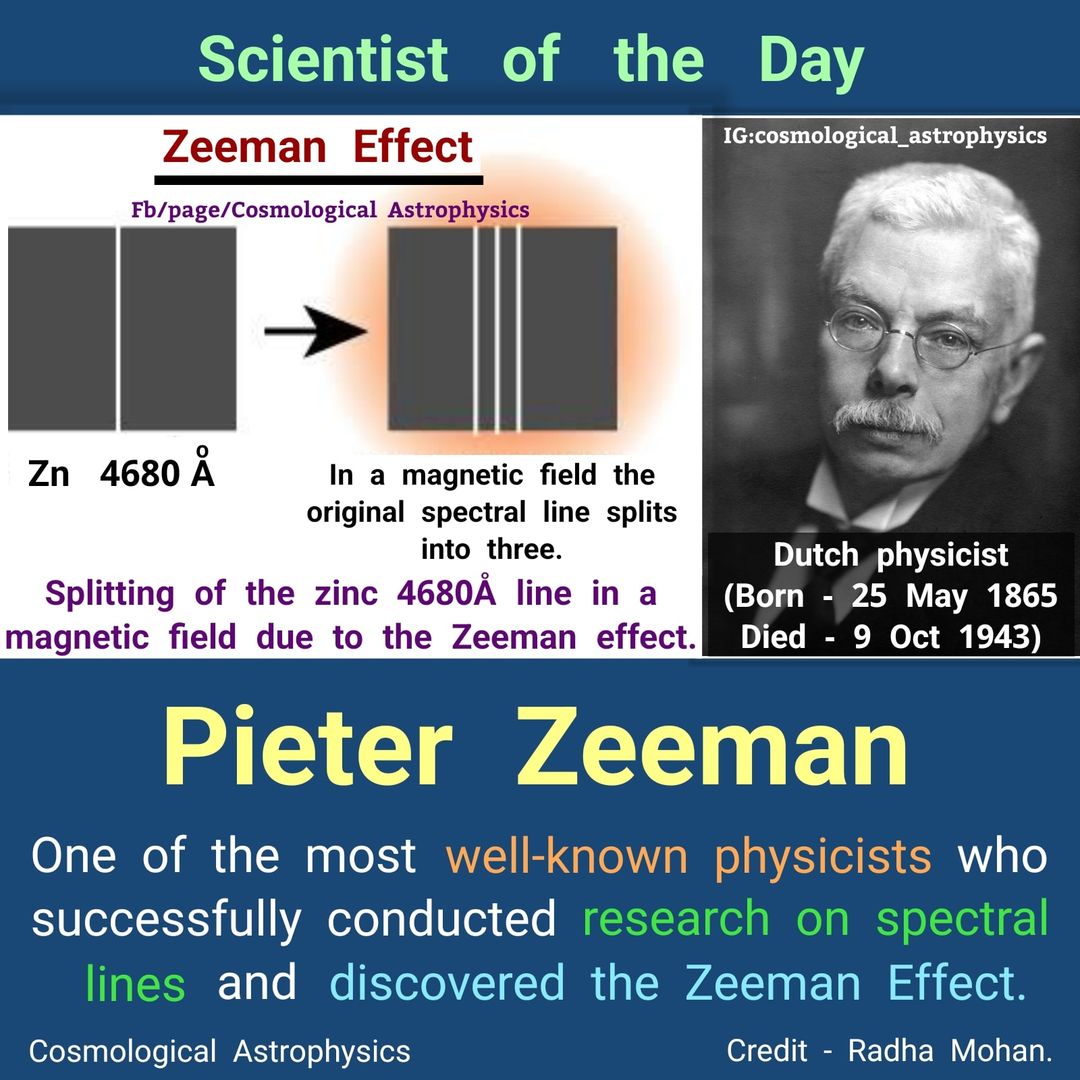
The Zeeman effect, is the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field. The Zeeman effect is very important in applications such as nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, electron spin resonance spectroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and Mossbauer spectroscopy. It may also be utilized to improve accuracy in Atomic absorption spectroscopy.
When the spectral lines are absorption lines, the effect is called Inverse Zeeman effect.
The Zeeman effect is named after the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman. [wikipedia, Zeeman Effect]
See Also
Aharonov-Bohm Effect
Bjerknes Effect
Chapter 8 - The Oneness of Gravity and Magnetism - II, page 178
Effect
Kervran Effect
Light
Ozone Effects
Placebo Effect
Table 13.03 - Photoelectric Effect of Elements
Rainbow
Spectra
spectrum - Keely mentions triple lines
Table of Cause and Effect Dualities
Tyndall Effect
14.11 - Ranges of Forces Effects and Actions
14.30 - Effect of Preponderance
15.24 - Water is Sensitive to Biometeorological Effects
16.11 - Seebeck Effect
2.22 - Voiding - an Effect of Desire and Will Force
